The Florida Climate Center serves as the primary resource for climate data, information, and services in the state of Florida.
What's new in our world?
The Florida Climate Center achieves its mission by providing climate monitoring, research, and expertise to be applied by the people, institutions, and businesses of Florida and the surrounding region.
We provide direct service by fulfilling requests for climate and weather data and information in a variety of formats.
We perform research that advances the understanding of the climate variability and changes of Florida and the surrounding region.
We provide outreach in presentations and at events aimed at a variety of groups, interests, and ages.
Prepared by Melissa Griffin and David F. Zierden. Special thanks to L. Zuromski.
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
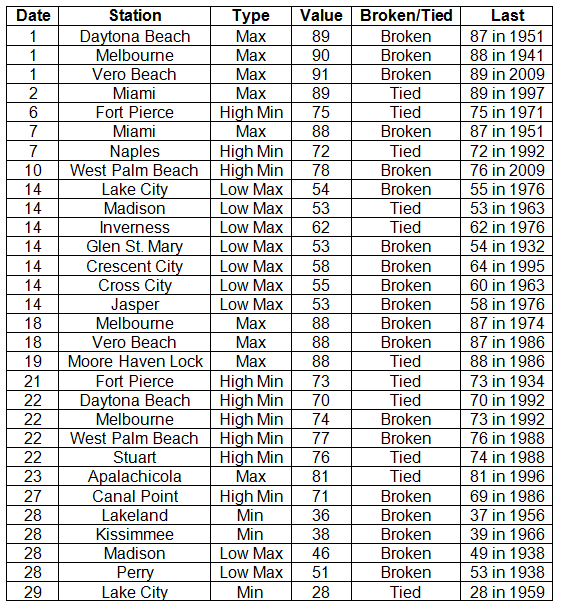
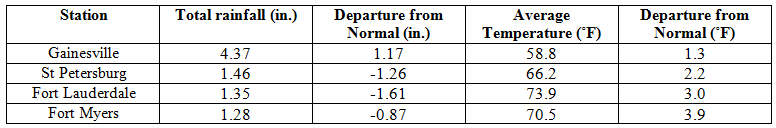
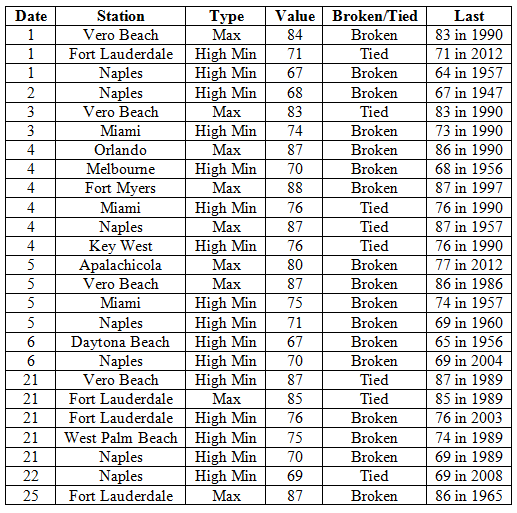
Average temperatures were above normal in February. In a complete turn around from cold of January 2014, the average temperatures for February 2014 were above normal across the entire state (Table 1 and Appendix 1). Departures from normal ranged from 0.9˚F in Jacksonville to 4.0˚F in Miami. The monthly average temperature for February 2014 was the 5th warmest in Miami, 7th warmest in West Palm Beach, and the 9th warmest in Vero Beach. Portions of the southeast coast saw more than 20 days with maximum temperatures above 80˚F and Naples recorded is warmest low temperature (71˚F) in the 1st two weeks of February since records started in 1942. There were multiple maximum and high minimum temperatures that were broken or tied (Appendix 2).
Table 1: February average temperatures and departures from normal (°F) for selected cities.
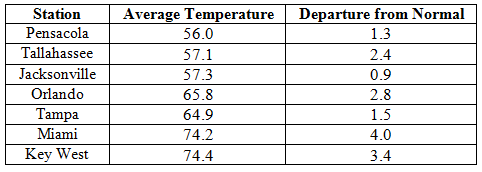
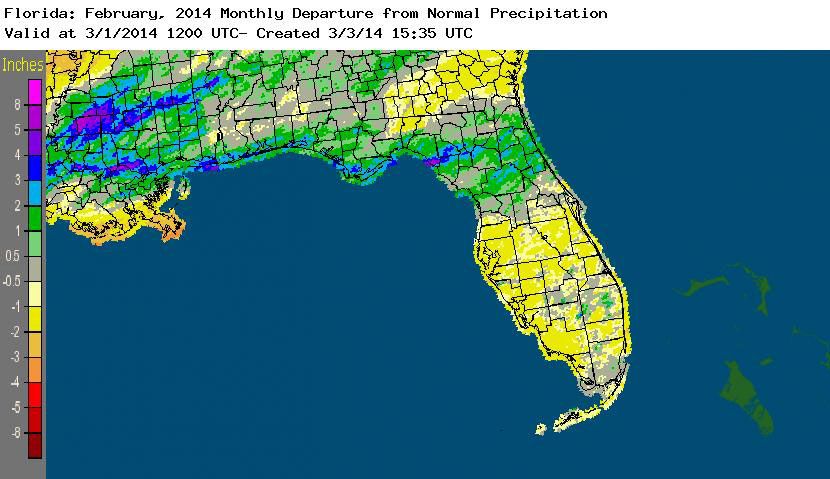
Rainfall totals varied across the state in February. Portions of the Big Bend and Panhandle, reported monthly rainfall totals near average or slightly above normal, while the rest of the state saw near to above average rainfall during February (Figure 1). Departures from normal roughly ranged from -1.61” to 2.82” (Table 2 and Appendix 1), though localized parts of Florida saw rainfall totals that were as much as 3.00” below normal to over 4.00” above normal. There was only one 24-hour precipitation record broken for the month (Table 3).
Table 2: February precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
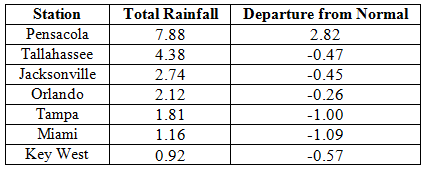
Table 3: Select daily rainfall records (inches) broken during February (compiled from NOAA, NWS).
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for February is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
ENSO-neutral conditions continue in the Pacific. Neutral ENSO conditions continue to be reported for the equatorial Pacific with the equatorial sea surface temperatures (SST) above average across in the western Pacific, with regions of below average SST in the eastern Pacific. ENSO-neutral conditions are favored to continue through the spring of 2014, with a potential El Nino forming in the summer. The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) predicts above normal temperatures across the entire state and below normal precipitation for the Florida Panhandle through May.
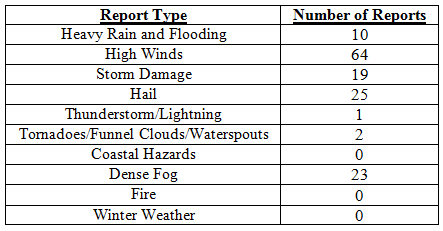
Hazardous weather events in February. There were 144 total severe weather reports were recorded in Florida for the month of February. The month started off with reports of dense fog on the 1st, 2nd and 3rd in portions of southern Florida. Areas south of Lake Okeechobee reported visibilities less than1/4 mile during the morning hours, impacting both inland and coastal communities. These same areas recorded dense fog on the morning of the 8th, with one report stating, “ Visibilities of 200-300 yards reported in Belle Glade.” A low-pressure system and associated stationary front on the 12t produced a line of thunderstorms that caused storm damage, with multiple reports of hail (pea to quarter sized), heavy rain high wind (up to 60 mph) as it pushed through the Peninsula. 73 storm reports came in from 15 counties on the 12th, with a report of a tornado in Fort Meade, FL that blew off a roof and porch of a structure, and lightning that started a house fire in Tampa, FL. A cold front raced through the northern part of the state on the 21st, producing high winds and hail along its path. There were multiple reports of trees and power lines down, with a report of an 18-wheeler being flipped over in Escambia County and a funnel cloud with 1” diameter hail in Putnam County. On the morning of the 23rd, an area of disturbed weather produced heavy rains, which caused flooding along portions of US 98 in Bay County, along with multiple reports of golf ball sized hail. Later on the 23rd, areas near Gainesville, Ocala, Daytona Beach and Orlando were impacted by hail and high winds from the same storm system.
Table 4: Breakdown of storm reports submitted in Florida during February (compiled from Southeast Regional Climate Center).
Agricultural and other climate-related impacts. The majority of the state saw temperatures that ranged from the upper 60s to the low 80s at the beginning of the month. The cold weather from the last week in January slowed the growth of winter wheat and caused a decline in the pasture conditions in northern parts of the state. The rain and foggy weather increased disease in vegetables, with reports of late blight being reported in tomatoes and potatoes. The citrus area received widespread rain and the active commercial groves in the state were drought free; but fruit sizes were still small on all varieties. Cloudy, cool wet conditions hampered fieldwork and crop growth by mid month. Various fruits and vegetables were marketed, while sugarcane and strawberries entered the last weeks of harvest. Citrus growers in Indian River experimented with tenting younger trees to help combat the psyllid population that had caused greening. The end of February saw farmers in Washington and Gadsden counties preparing ground for peanut and corn planting. Grover managers were reporting various sizes in the same blocks and have noticed blooms in several of the more southern citrus growing areas, signaling the beginning of next year’s crop. Citrus greening was still an issue and preventative measures were being taken to protect unaffected trees. Cattle conditions during the month were good, while pasture conditions were mostly fair; promoting cattlemen to feed hay and supplements.
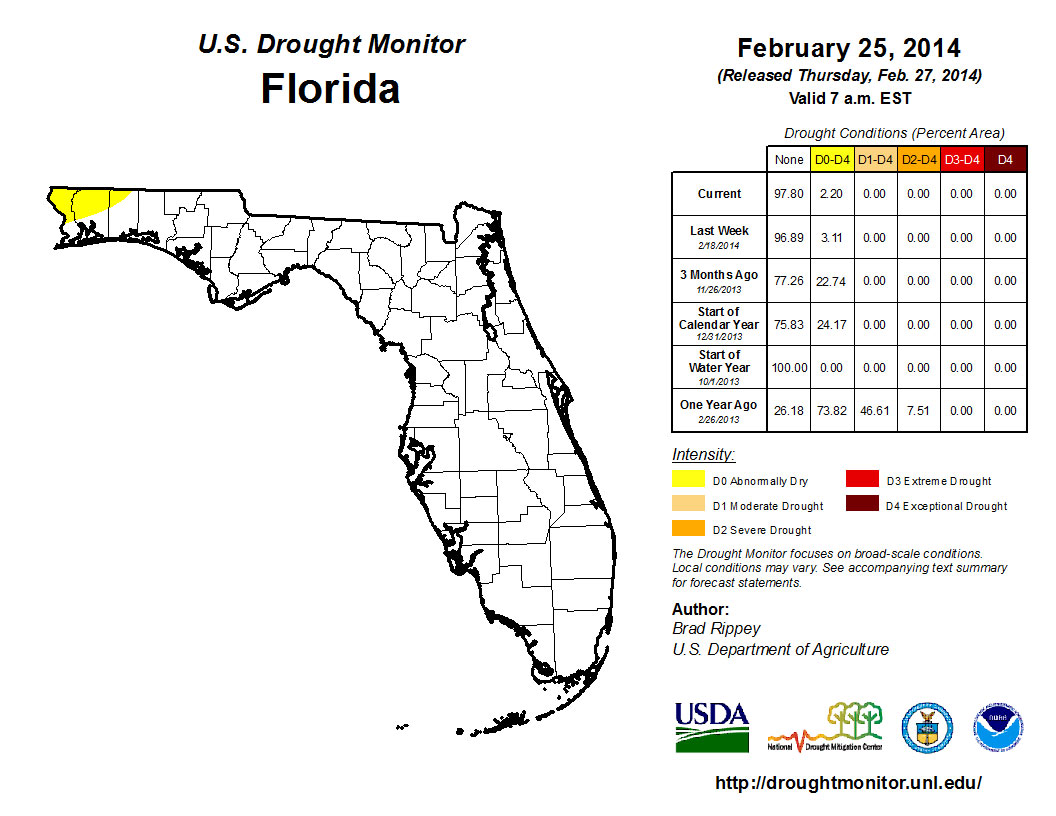
At the end of January nearly 30% of the state was characterized as dry, with the main concentration of the dryness (D0) confined to portions of the Space Coast and through the Okeechobee watershed into interior portions of the state to southwestern coast from Lee to Collier counties; and there was a small area of dryness reported in Escambia and Santa Rosa counties. Rains in the early part of the month eased most of D0 conditions in the Peninsula, with only Volusia, Seminole, Orange and Brevard counties showing dry conditions on the February 4th release of the Drought Monitor. By the 18th of the month, rainfall over portions of the east coast had led to an improvement of the lingering dry conditions and the only dry conditions left in the sate at the month’s end were those in the northwest Panhandle. The Climate Prediction Center is forecasting for precipitation to be below normal for March, April and May, in the Panhandle, while else where, precipitation is expected to be near normal as the state begins the transition in to the dry spring season.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of February 25, 2014 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix 1: Additional February departures from normal data for Florida locations.
Prepared by Melissa Griffin and David F. Zierden.
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
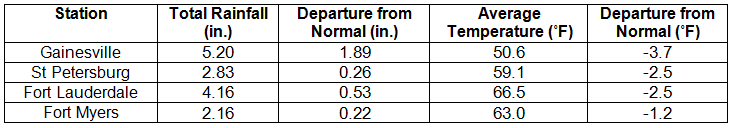
Average temperatures were below normal in January. The average temperatures for January 2014 were colder than normal across the entire state (Table 1 and Appendix 1). Departures from normal ranged from -0.2 ˚F in Key West to -5.4˚F in Pensacola. The monthly average temperatures for January 2014 were the 5th coldest in Madison and Pensacola, 7th coldest in Lake City, 8th coldest in Clermont, and 9th coldest in Gainesville, Inverness, and Orlando. On the 7th of January, a bitterly cold air mass pushed through the state, and locations north of Avon Park, with the exception of a few coastal stations, did not reach the 50˚F mark. Portions of the state, mainly in the Panhandle, did not get above 40˚F on the 29th. While there were a number of low maximum and minimum temperatures tied and broken during the month (121), there were also multiple maximum and high minimum temperatures that were broken or tied (Appendix 2).
Table 1: January average temperatures and departures from normal (°F) for selected cities.
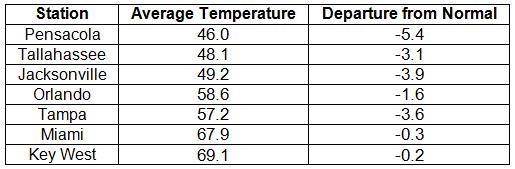
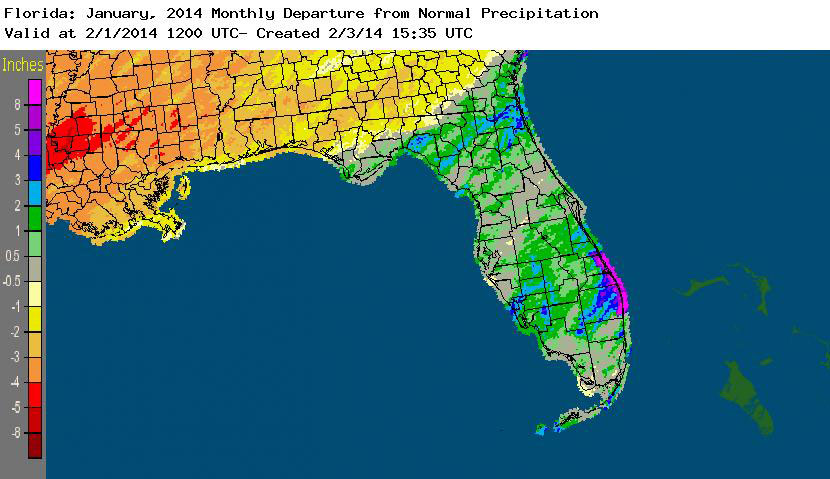
Rainfall totals varied across the state in January. Portions of the Big Bend and Panhandle reported monthly rainfall totals below normal, while the rest of the state saw near to above average rainfall during January (Figure 1). Departures from normal roughly ranged from -1.18” to 4.64” (Table 2 and Appendix 1), though some areas of Florida saw rainfall totals that were as much as 4.00” below normal to over 8.00” above normal. There was a report of 22.20” of rainfall measured in Hypoluxo on January 9 – 10 from torrential downpours associated with a stalled front over portions of the east coast. Totals across the area ranged from 10 to 15”. January 2014 was the wettest on record in Fort Pierce, 3rd wettest in Melbourne, 4th wettest in West Palm Beach, 6th wettest in Jacksonville and Key West, and 10th wettest in Gainesville and Miami. There was 1” of snow reported in Pensacola on the 28th. Numerous 24-hour precipitation records were broken for the month (Table 3).
Table 2: January precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
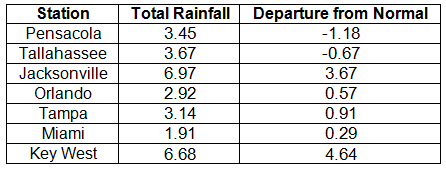
Table 3: Select daily rainfall records (inches) broken during January (compiled from NOAA, NWS).
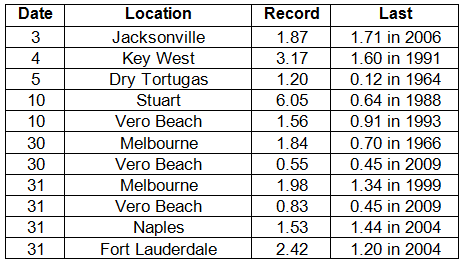
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for January is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
ENSO-neutral conditions continue in the Pacific. Neutral ENSO conditions continue to be reported for the equatorial Pacific, with the equatorial sea surface temperatures (SSTs) near average across much of the equatorial Pacific and regions of below average SSTs in the east-central Pacific. ENSO-neutral conditions are favored to continue through the summer of 2014. NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center (CPC) predicts above normal temperatures and below normal precipitation for the entire state through April.
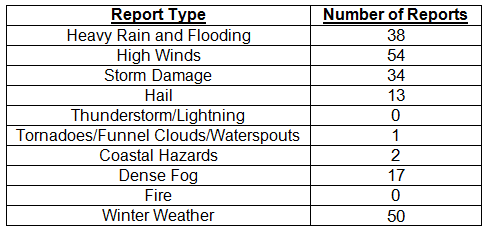
Hazardous weather events in January. 209 severe weather reports were recorded in Florida for the month of January; 50 of those reports were for winter weather — something that does not happen often in the state. The month started off with dense fog reported on the southern shore of Lake Okeechobee, which reduced visibilities to less than ¼ mile. Also on the 2nd, heavy rain and high winds were seen along parts of the northeast coast. Reports of non-thunderstorm-based high winds came in along the Florida Keys from the 5th through the 7th. Localized flooding and heavy rain were reported from Boca Raton to Stuart, when a cold front ‘backed up’ and funneled tropical moisture over the area, producing heavy rain rates (~15.00” in 3 hours) on the 9th and 10th. On the 11th, multiple reports of storm damage and high winds were made as thunderstorms pushed through the Big Bend and north Florida. A storm on the 21st produced hail (pea to quarter sized) along its track from Normandy, FL, to Jacksonville. Widespread dense fog was reported on the mornings of both the 27th and 28th for areas south and southeast of Lake Okeechobee. The end of the month saw the first widespread winter weather events for the state in over a decade, as reports of freezing rain, sleet, and snow were made across the entire northern part of the state. Accumulating freezing rain caused Interstate 10 to be closed from the Florida/Alabama line to just east of Tallahassee. Many school districts, businesses, and government offices closed for ‘snow days’ from the 28th through the 30th due to the icy conditions.
Table 4: Breakdown of storm reports submitted in Florida during January (compiled from Southeast Regional Climate Center).
Agricultural and other climate-related impacts. Most of Florida reported rainfall and average temperatures at the beginning of January, which allowed for final harvesting of soybeans in the northern part of the state and the sugarcane to be processed without issue in Hendry, Palm Beach, and Glades counties. There was some frost and fungal damage to strawberries, collards, and turnips in Nassau County, and field workers were still reporting small sizes in all citrus varieties. The arctic air mass that impacted the state in early January did cause small damage to winter oats and contributed to pasture decline, while the winds associated with the cold front battered vegetable crops in Charlotte, Collier, Hendry, and Lee counties. Cold temperatures toward the end of the month caused some damage in cold-prone areas with frosted tops on plants, and there were losses in Bradford County due to frost and lower temperatures. Winter cover crops were being planted in the Panhandle. During the month, cattle and pasture conditions remained fair, though the prolonged dry conditions caused poor pasture conditions, and cattlemen used hay and supplements across the state to supplement forage.
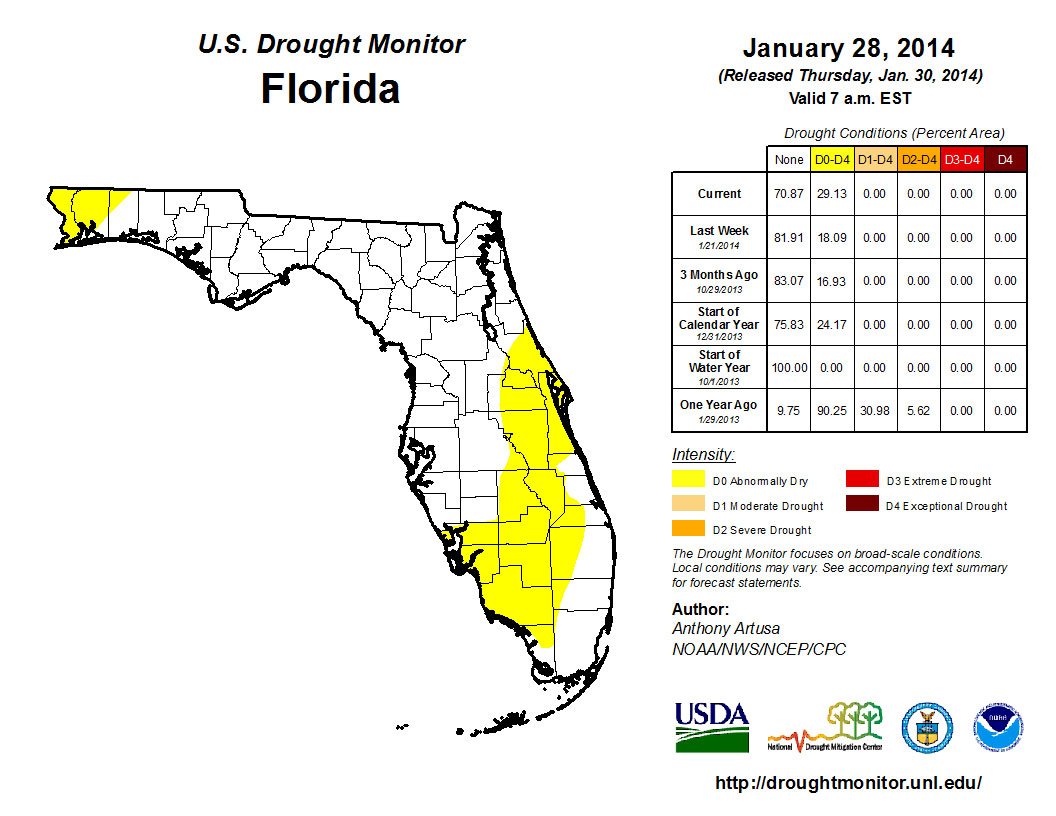
The beginning of 2014 saw dry conditions reported in 25% of the state, with the main concentration of the dryness (D0) confined to portions of the Space Coast and through the area of the state known as the Florida Heartland (DeSoto, Glades, Hardee, Hendry, Highlands, and Okeechobee) to Collier County. The residual dry conditions that were in northern Santa Rosa County and along the Florida-Georgia line near Jacksonville were removed after rainfall early in the month. Conditions remained consistent through most of January, although, by the end of the month, the area of dryness along the east coast and peninsula had expanded to cover more of the interior of the state. D0 was reintroduced into portions of Escambia and Santa Rosa counties in the Panhandle on the 28th. The Climate Prediction Center is forecasting below normal precipitation for February, March, and April, which could limit the amount of rain received by northern parts of the state during a critical recharge season.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of January 28, 2014 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix 1: Additional January departures from normal data for Florida locations.
Prepared by Melissa Griffin and David F. Zierden.
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
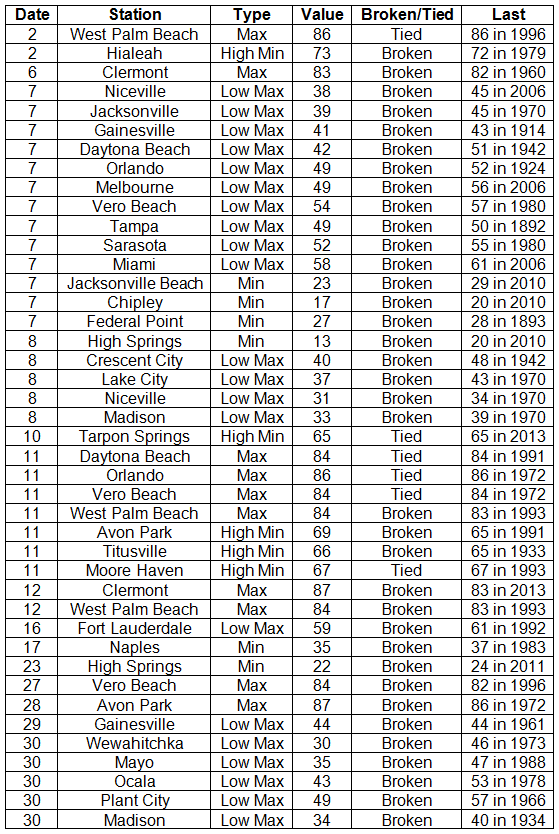
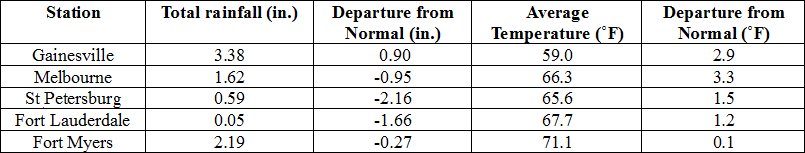
Average temperatures were above normal across the state in December. The departures for average temperatures in December 2014 for the Peninsula were above normal, though most of the reporting stations in the northern part of the state saw average temperatures well above normal. The departures ranged from 0.8˚F in Miami to 3.9˚F at Tallahassee. (Table 1 and Appendix 1). Despite the warm month, some stations in the Panhandle, Big Bend and North Florida recorded at least one day with a minimum temperature below freezing (32˚F) during the month; and no stations reported a maximum temperature over 90˚F. Multiple temperature records were tied or broken across the state in December (Appendix 2).
Table 1: December average temperatures and departures from normal (˚F) for selected cities.
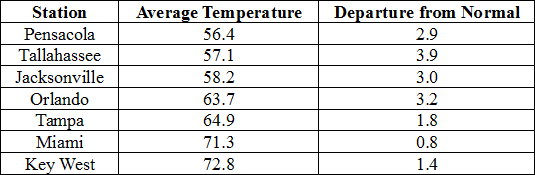
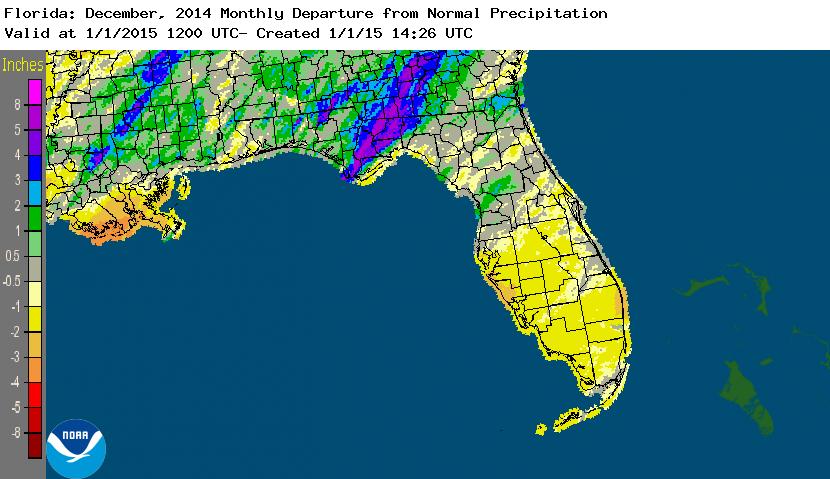
Rainfall totals varied across the state in December. A very localized portion of the Big Bend reported monthly rainfall totals well above normal, while the rest of Florida saw average rainfall during December near to below normal (Figure 1). Departures from normal roughly ranged from -2.16” to 4.88” (Table 2 and Appendix 1), though localized parts of Florida saw rainfall totals that were as much as 4.00” below normal to over 8.00” above normal (Figure 1). Tallahassee reported its wettest day in December since records started in 1892 on the 23rd when 7.44” of rainfall was recorded. 2014 was the 9th wettest year in Pensacola (83.17”) and the 10th wettest year in Daytona Beach (63.77”). There were multiple 24-hour precipitation records broken for the month (Table 3).
Table 2: December precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
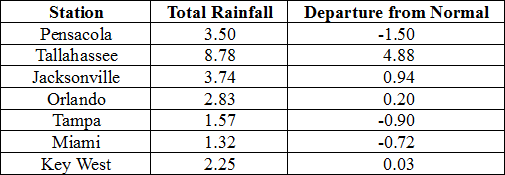
Table 3: Select daily rainfall records (inches) broken during December. (Compiled from NOAA, NWS)
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for December is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
ENSO-Neutral Conditions Continue in the Pacific.
Based on current data and forecast models, the Climate Prediction Center (CPC) continue to have an El Niño Watch in place. Though Neutral ENSO conditions continue to be reported, positive sea surface temperatures (SST) anomalies have been recorded across most of the Pacific Ocean. An El Niño event is favored to develop during the Northern Hemisphere winter. CPC predicts below normal temperatures and above normal precipitation across the state through March 2015.
Hazardous Weather Events in December.
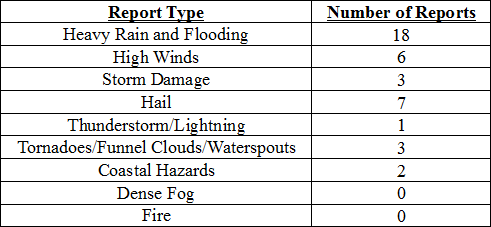
There were only 40 hazardous weather reports across the state in December. On December 8th, high winds (up to 50 mph) were reported along the eastern coast of Florida. High surf, up to 8 feet was reported around the area of St. Augustine and Vilano Beach. Waterspouts were reported offshore of Miami Beach, FL on the 13th. A lightning strike injured 11 people near Raymond James Stadium (Tampa, FL) on Dec 21st prior to a NFL Football game. Seven people were transported to the hospital, one of which was reported in critical condition, while four additional people went to the hospital on their own. A severe thunderstorm produced hail (pea to golf ball sized) in the Gainesville and Middleburg areas on the 22nd. On December 23rd, torrential heavy rains caused flooding in Tallahassee and Quincy, FL. Many roads in both locations were impassable due to standing water. In Defuniak Springs, a 10’ swath of water covered the southbound lanes of Highway 83, and floodwaters had closed roads in Walton County. After the front passed through, the combination of soggy ground and high winds caused trees to be knocked down in multiple Panhandle locations.
Table 4: Breakdown of storm reports submitted in Florida during the month of December (Compiled from Southeast Regional Climate Center.)
Agricultural and other climate related impacts.
At the beginning of December, cotton and soybean harvesting wrapped up in the Panhandle and north Florida. Farmers in the area began planting winter forage, oats and wheat for grain. The sugarcane harvest in Glades and Hendry counties continued, while vegetables harvesting in southwest Florida ramped up. Small amounts of rain and warmer weather improved pasture conditions and reduced cattle stress across portions of the state. Early orange harvest picked up significantly in the first part of the month, and the grapefruit harvest for both white and colored headed to plants for processing or to the fresh market. By mid-month, some U-pick strawberry fields had opened in Orange County, and spring vegetable planting began in Flagler and Putnam counties. Cattle and horse owners in southwest Florida were feeding hay to livestock, though pasture conditions were reported fair to good across Florida. Most of the early orange harvest was being used for juice and 13 out of 15 processing plants had opened and were beginning to run fruit. Heavy rains at the end of the month caused the fieldwork to be halted in the Panhandle, and the coldest temperature reported during that time was 34˚F in Walton County (Defuniak Springs). Sugarcane, strawberries, citrus, and vegetable harvests continued across the state. Harvesting totals for early oranges were down due to small sized fruits and the holidays. Citrus grove activity for the month included irrigation, mowing, aerial spraying, and fertilizing.
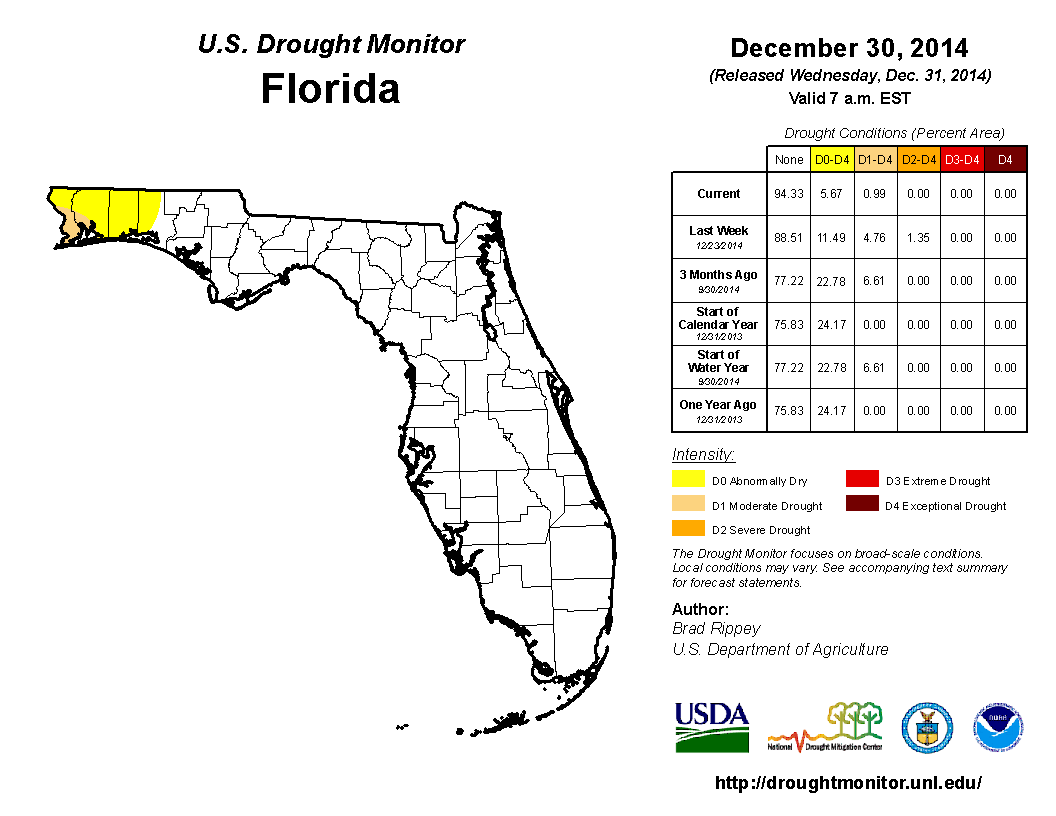
At the end of November, heavy rains across portions of the Panhandle and Big Bend reduced the moderate drought (D1) conditions to abnormally dry (D0) in Gadsden, Leon, Jefferson and Wakulla counties. Dry conditions over the first part of the month of December kept drought conditions consistent across the state. When the Drought Monitor was released on the 16th of the month, the D0 conditions were removed from Gadsden, Jefferson, Leon and Wakulla counties. Unfortunately, the rains that helped ease the drought conditions that had plagued that portion of the Big Bend for months did not help the northwestern Panhandle. The D0 conditions were seen in Bay, Holmes, Jackson and Washington counties, and D1 conditions expanded from the coastal area to interior portions of Escambia, Okaloosa and Santa Rosa counties. Severe drought (D2) was introduced in Escambia and Santa Rosa counties at mid-month. On December 23rd – 24th, a strong storm system moved through the northern part of the state, dumping 3.00” to 10.00” in the Panhandle and Big Bend. The rainfall caused localized flooding in some urbanized areas and some rivers and streams to rise. In addition, the rainfall reduced some of the drought impacts in the northwestern Panhandle counties. The remainder of the state saw monthly rainfall totals slightly below normal, though no drought conditions were posted during December.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of December 31, 2014 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix 1: Additional December Departures from Normal Data for Florida Locations
Appendix 2: Select daily maximum and minimum temperature records (o F) tied or broken during December. (Compiled from NOAA, NWS)
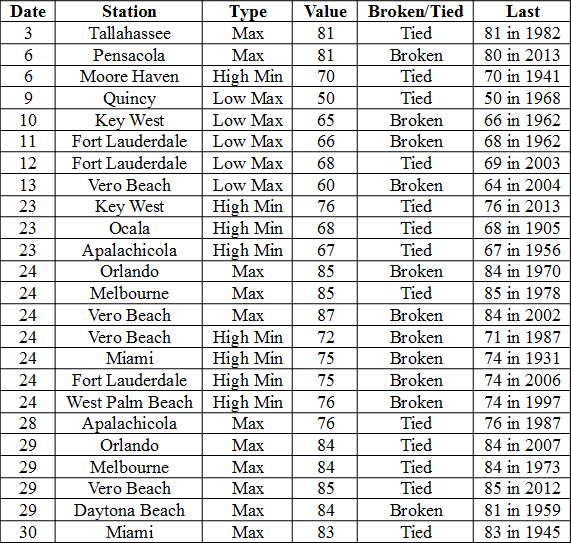
Prepared by Melissa Griffin and David F. Zierden.
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
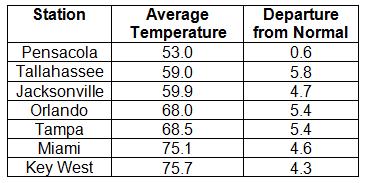
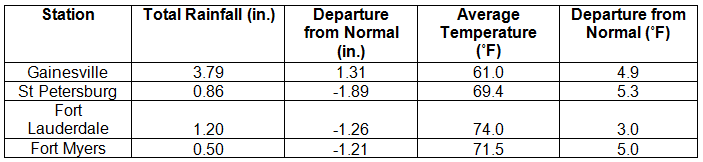
Average temperatures above normal across the state in December. December 2013 was a fairly warm month across Florida (Table 1 and Appendix 1). Departures from normal ranged from 0.6 ˚F in Pensacola to 5.8˚F in Tallahassee. Average temperatures for December 2013 were the 2nd warmest in Miami and Fort Lauderdale, 3rd warmest on record in Orlando and Daytona Beach, 5th warmest in Key West and Tampa, and 10th warmest in Tallahassee. There were a number of maximum and high minimum temperatures tied and broken during the month (Appendix 2). The all-time record high maximum temperature for December in Jacksonville was tied on the 9th with a recorded temperature of 84˚F.
Table 1: December average temperatures and departures from normal (°F) for selected cities.
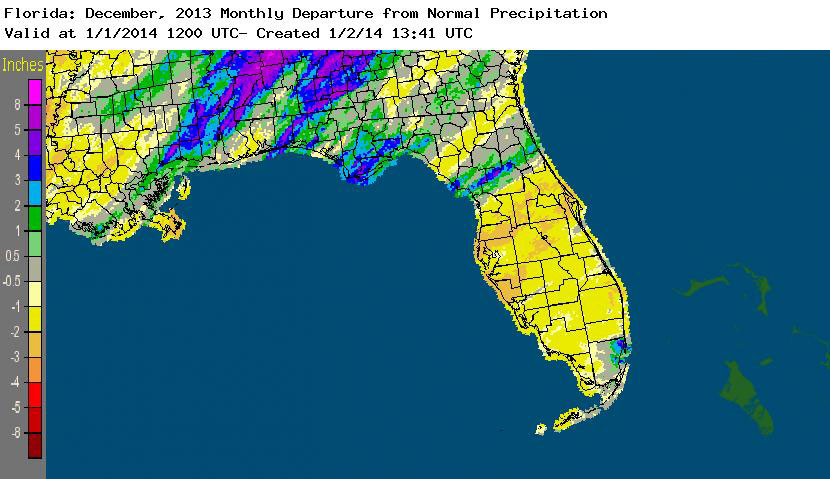
Rainfall totals varied across the state in December. Portions of the Big Bend, Panhandle, north-central Florida, and areas around Miami reported monthly rainfall totals above normal, while the majority of the Peninsula saw below normal totals (Figure 1). Departures from normal roughly ranged from -2.31” to 2.63” (Table 2 and Appendix 1), though some areas of Florida saw rainfall totals that were as much as 3.00” below normal or nearly 8.00” above normal. December 2013 was the 6th wettest December on record in Miami, while it was the 6th driest in Orlando. Numerous 24-hour precipitation records were broken for the month (Table 3).
Table 2: December precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
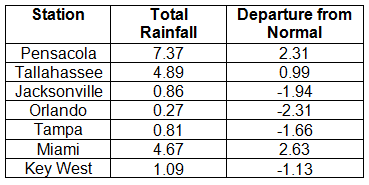
Table 3: Select daily rainfall records (inches) broken during December (compiled from NOAA, NWS).
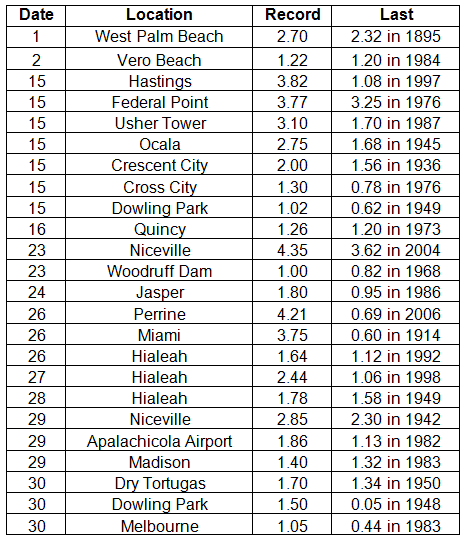
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for December is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
ENSO-neutral conditions continue in the Pacific. Neutral ENSO conditions continue to be reported for the equatorial Pacific, with equatorial sea surface temperatures (SST) near average across much of the equatorial Pacific. ENSO-neutral conditions are favored to continue through the summer of 2014. The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) predicts above normal temperatures in the Panhandle, normal temperatures for the rest of the state, and below normal precipitation for the entire state through March.
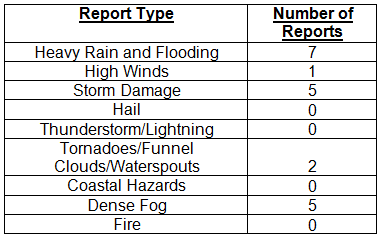
Hazardous weather events in December. Only 20 severe weather reports were made across the state in December. Heavy rain was reported in and around the Vero Beach area on the 1st, with 5.46” of rain reported in almost 4 hours. Dense fog was reported in Tallahassee on the 6th with visibility less than 1/8 of a mile, and widespread dense fog was observed on the west side of Lake Okeechobee in La Belle, Clewiston, and Immokalee on the 7th. Straight-line winds, estimated at 100 mph and associated with a thunderstorm north of Ocala, caused damage in Anthony, FL, where a barn was moved off its concrete foundation on the 14th. On the same day, an EF1 tornado moved through Palm Coast, (Flagler County, FL), uprooting trees and damaging power lines along its path. The day after Christmas, heavy rain was reported in between Homestead and Miami; early in the morning on the 29th, high winds from a thunderstorm were reported at Mexico Beach, FL.
Table 4: Breakdown of storm reports submitted in Florida during the month of December (compiled from Southeast Regional Climate Center).
Agricultural and other climate related impacts. In December, rain was limited across the state, and farmers in the northern part of the state were finishing up harvest of cotton, soybeans and continued planting oats, wheat, and rye. Light frost during the month ended the warm season perennial pastures in the Panhandle. Cattlemen were feeding hay and supplements to stock as pasture conditions ranged from poor to good condition and winter grazing was stressed due to drought. Irrigation in the citrus region continued as dry conditions persisted, and workers were reporting small-sized fruits in all varieties. The warmer-than-normal temperatures led to accelerated vegetable growth in many south Florida counties, and sugarcane harvesting proceeded on schedule.
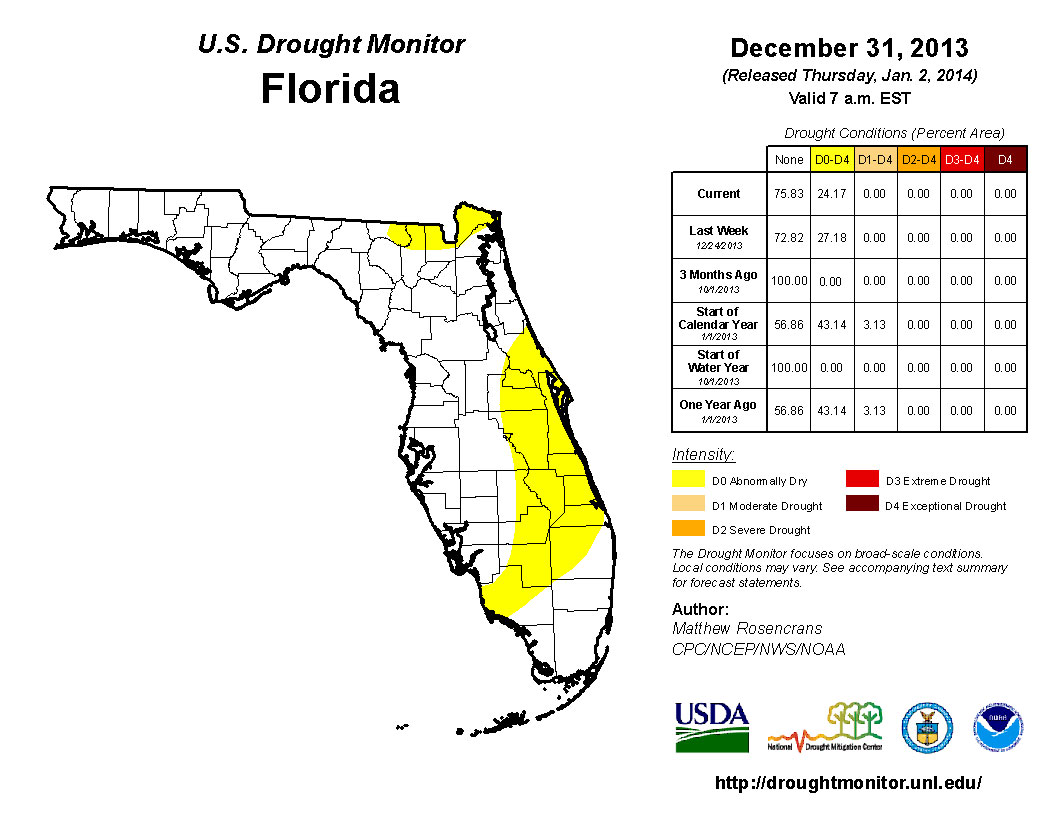
Early in December, there was an expansion of dry conditions (D0) in south Florida to include portions of Collier and Lee counties. The lack of rain in the beginning of December caused the introduction of D0 into the northwest Panhandle (Escambia, Santa Rosa and Okaloosa counties) and in part of central Florida (Orange, Osceola, Seminole and Volusia counties). However, rain in the northeastern portion of the state alleviated some of the dryness around the areas of Jacksonville, St. Augustine, Ocala and Gainesville. Some residual dryness remained in Nassau, Baker, Columbia and Hamilton counties by the end of the month, with D0 conditions still present along portions of the east coast and citrus growing region. The CPC forecast for the next three months (January, February, and March) is predicting below normal rainfall, so the chance of seeing more dry conditions, and potentially drought, introduced into the state remains high.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of December 31, 2013 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix 1: Additional Decemer departures from normal data for Florida locations.
Prepared by Melissa Griffin and David F. Zierden.
Special thanks to Lauren Zuromski.
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
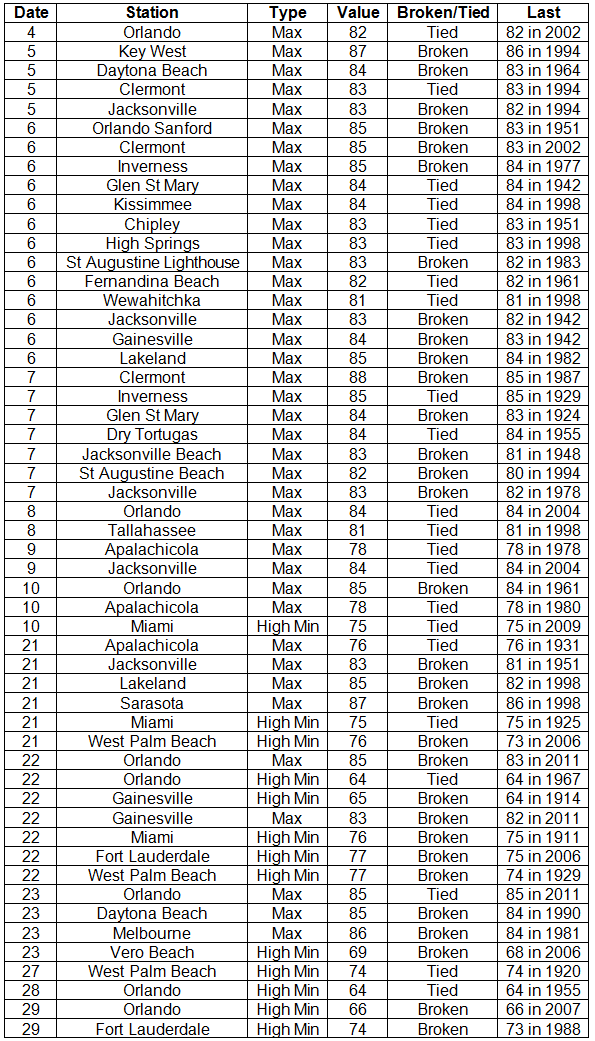
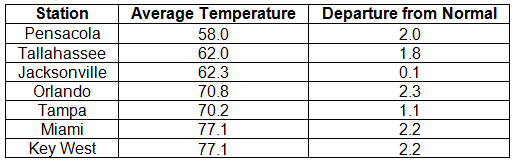
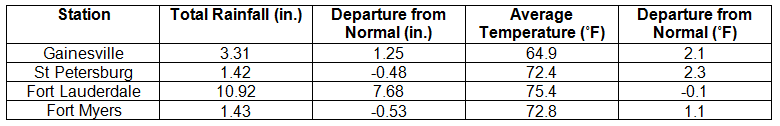
Average temperatures above normal across the state in November. The majority of stations across the state reported above normal average temperatures during November, though a few stations saw temperatures that were slightly below normal (Table 1 and Appendix 1). Departures from normal ranged from -0.1˚F in Ft. Lauderdale to 2.3˚F in Orlando and St. Petersburg. Average temperatures for November 2013 were the 3rd warmest on record in Miami and the 10th warmest in Orlando. There were a number of low maximum and high minimum temperatures tied and broken during the month (Appendix 2). The all-time record high maximum temperature for November in Daytona Beach was tied on the 1st with a recorded temperature of 89˚F. This tied the record that was set on November 28, 1948.
Table 1: November average temperatures and departures from normal (°F) for selected cities.
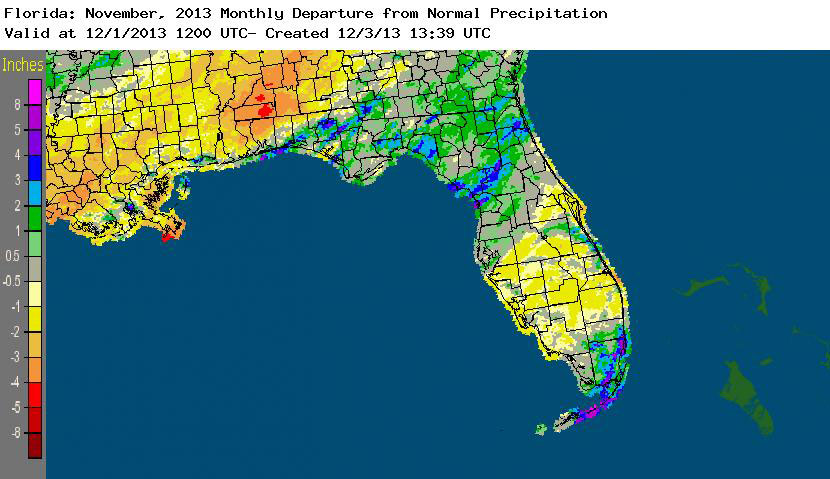
Rainfall totals varied across the state in November. Portions of the Big Bend, North Florida, and areas along the southeast coast and Florida Keys reported monthly rainfall totals above normal, while extreme northwest Florida and most of the southern Peninsula saw below normal totals (Figure 1). Departures from normal roughly ranged from -0.59” to 7.68” (Table 2 and Appendix 1), though some areas Florida saw rainfall totals that were as much as 5.00” below normal or nearly 8.00” above normal. November 2013 was the 4th wettest November on record in Fort Lauderdale, 7th wettest in Chipley, and 10th wettest in Miami. Numerous 24-hour precipitation records were broken for the month (Table 3), including one record that was tied that dates back to 1890 in Key West.
Table 2: November precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
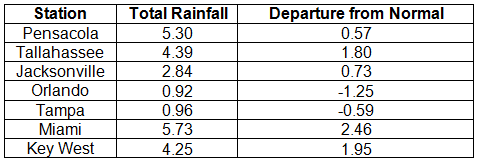
Table 3: Select daily rainfall records (inches) broken during November (compiled from NOAA, NWS).
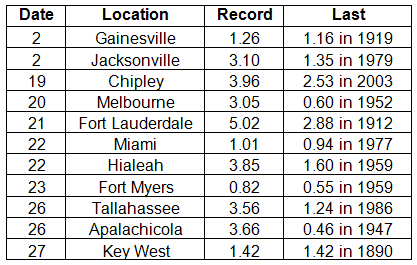
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for Novemer is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
ENSO-neutral conditions continue in the Pacific. Neutral ENSO conditions continue to be reported for the equatorial Pacific, with equatorial sea surface temperatures (SST) near average across much of the equatorial Pacific. ENSO-neutral conditions are favored to continue through the spring of 2014. The Climate Prediction Center (CPC) predicts normal temperatures and precipitation for the state through February.
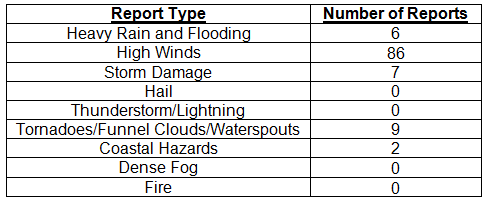
Hazardous weather events in November. Only 110 severe weather reports were made across the state in November. On the 5th, high winds with gusts up to 50 mph, not associated with thunderstorms, were reported along the Florida Keys. Flooding was recorded in Fernandina Beach and Mayport, due to the astronomical high tides on the 5th and 6th. The passage of a strong cold front on the 13th and 14th produced strong winds across the eastern part of the state. Wind gusts of up to 45 mph were reported in Jacksonville Beach, St. Augustine, New Smyrna Beach, Key Biscayne, and Key West. Non-thunderstorm winds knocked down trees and power lines in Flagler Beach, Palm Coast, and St. Augustine. Multiple reports of waterspouts were made from Miami Beach and Fort Lauderdale on the 20th. Urban and street flooding was seen in Hallandale and Hollywood on the 21st and in Miami Lakes and North Miami Beach on the 23rd. Another strong cold front pushed through the state on the 24th, bringing another round of strong winds (gusts up to 45 mph) to portions of the eastern coast of the state. On the 26th, an area of low pressure moved east across the Panhandle before moving up the Eastern Seaboard. Strong thunderstorms caused storm damage in Shadeville and Tallahassee, with multiple reports of trees down in both locations. A supercell thunderstorm produced an EF1 tornado in Stonemill Creek (Gulf County) that damaged trees and a few building along its 3-mile long path. The same supercell produced tree damage in Red Hill (Liberty County).
Table 4: Breakdown of storm reports submitted in Florida during the month of November (compiled from Southeast Regional Climate Center).
Agricultural and other climate related impacts. Topsoil and subsoil moisture levels were down from October, with only 55-60% at adequate or surplus levels at the beginning of the month. Winter grazing was planted in Gulf and Jackson counties, while peanut and cotton harvesting continued in parts of northern Florida. Vegetable harvesting continued in central Florida, while land preparation and planting continued in south Florida. Disease/pests were causing poor pasture conditions in parts of the state, though the cooler and drier weather also played a role in limiting pasture growth. Activity in the citrus growing region began to ramp up, with inconsistent sizes reported between oranges (golf ball to baseball sized) and grapefruit (larger than baseball), which were still smaller than normal. Dry conditions through the first part of November led to a decrease in soil moisture levels, both in topsoil and subsoil. Winter grazing was stressed in Jefferson County due to the lack of rain. Hay, sugarcane and vegetables continued to be harvested through central Florida. By the end of the month, topsoil moisture levels were 40% short and 45% adequate, and subsoil moisture levels had rebounded to 24% short and 61% adequate. Pasture and cattle conditions were fair to good (90% for both) statewide, despite the lack of rainfall. Widespread rain in the citrus growing areas helped, though the fruit size was small on early and midseason oranges.
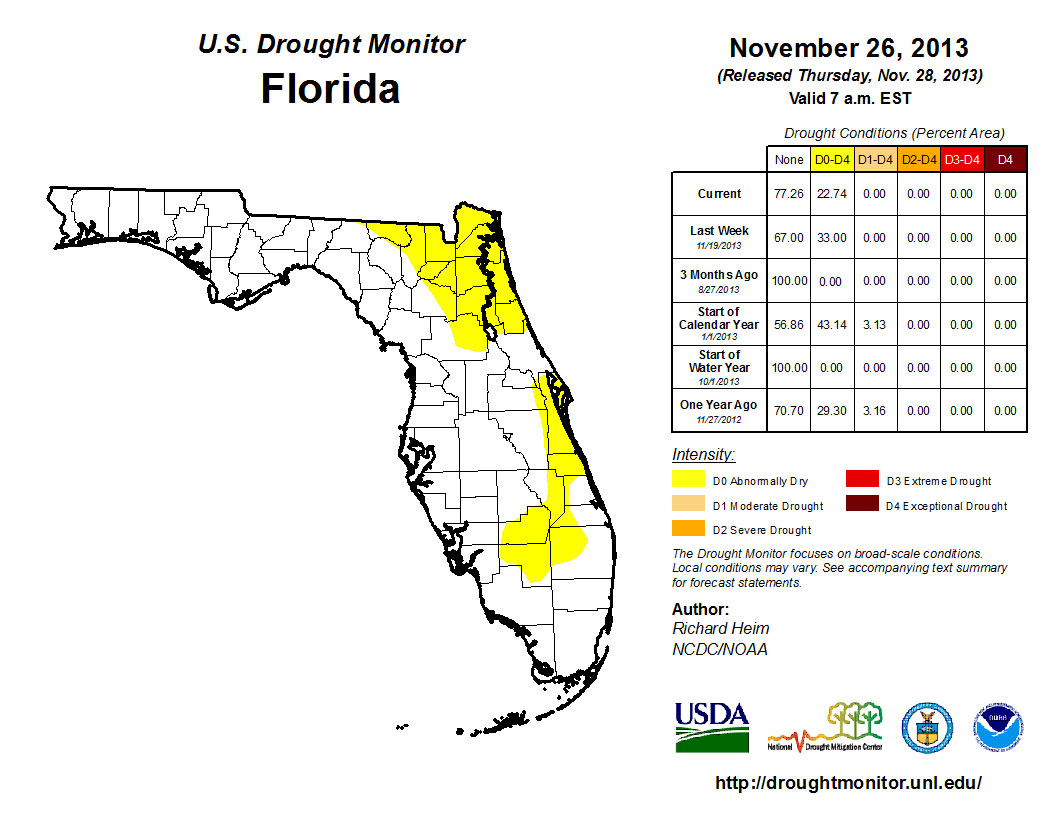
When the Drought Monitor was released on the 5th of November, the dryness from the previous week’s map (October 29th) had expanded and was reported along the Gold Coast and Monroe County, including the Florida Keys. By November 19th, all of the counties on the East Coast were reporting abnormally dry (D0) conditions. The D0 was also recorded in and around Lake Okeechobee and in portions of northern Escambia County. Rains in South Florida between the 19th and 26th eased the dryness along the immediate East Coast from Indian River through the Florida Keys. Throughout the entire month, the D0 conditions in North Florida were present, and even above normal rainfall for November in some of the area was not enough to ease drought concerns in that portion of the state. The CPC forecast for the next three-months is predicting below normal rainfall, so the chance of seeing more dry conditions, and potentially drought, introduced into the state remains high.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of November 26, 2013 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix 1: Additional November departures from normal data for Florida locations.
Appendix 2: Select daily maximum and minimum temperature records (° F) tied or broken during November (compiled from NOAA, NWS).