Prepared by Melissa Griffin, Preston Leftwich, and David F. Zierden
Florida Climate Center
The Florida State University
Tallahassee, FL
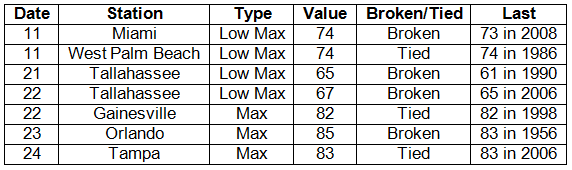
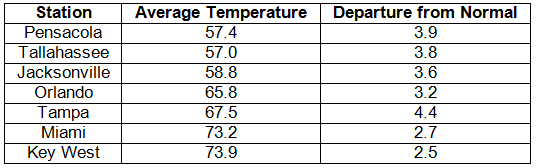
Average temperatures were above normal in December. Average temperatures were well above normal across the entire state (Table 1). Departures from normal ranged from 2.5°F at Key West to 4.4°F at Tampa. Unlike the previous two Decembers, there was very little cold air that made it into the state, which led to the warmer than normal temperatures that are typically reported with La Niña conditions. Miami had its 8th warmest December on record, while Tampa had its 9th, and both Orlando and Pensacola had their 11th. All of the temperature records broken for the month were either maximum high temperatures or record high nighttime low temperatures.
Table 1: December average temperatures and departures from normal (° F) for selected cities.
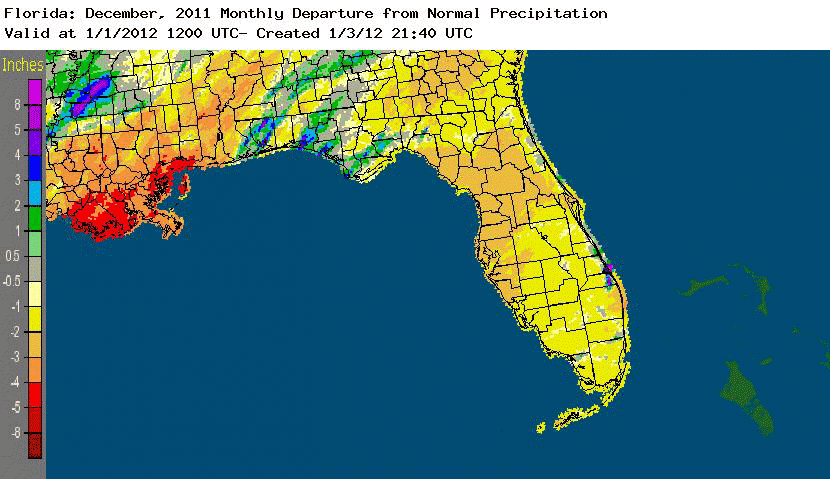
Rainfall totals varied statewide in December. Rainfall totals varied across the state during December (Table 2). Portions of the Panhandle had above normal rainfall, while most locations in the Peninsula recorded below normal precipitation. The month was the 5th driest on record at Tampa, while it was the 5th wettest on record at Pensacola. Most of the rainfall for the month reported at Pensacola came from two separate events, which broke daily rainfall records on the 20th and 26th (Table 3). The below normal rainfall for the month across most the state led the U.S. Drought Monitor to designate dry conditions in the Peninsula. Areal patterns of monthly rainfall relative to normal are depicted in Figure 1.
Table 2: December precipitation totals and departures from normal (inches) for selected cities.
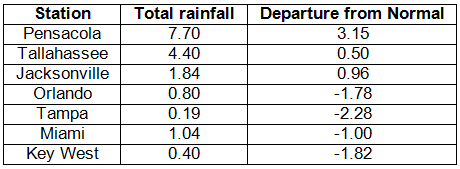
Table 3: Daily rainfall records (inches) broken during December (compiled from NOAA, NWS).
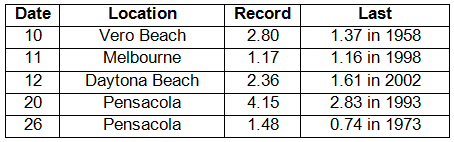
Figure 1: A graphical depiction of the monthly rainfall departure from normal (inches) for December is given in the figure below (courtesy of NOAA, NWS).
La Niña continued during December. La Niña conditions continue to be present across the equatorial Pacific, with sea surface temperatures (SST) at least 0.5?C below average for the region. The atmospheric circulation anomalies and winds are consistent with La Niña. The current La Niña is forecasted to continue through the winter of 2011/2012 into the spring, with the possibility of a return to neutral conditions by the summer. The Climate Prediction Center has predicted warmer than normal temperatures and below normal precipitation during this La Niña. The Arctic Oscillation (AO) remained positive during December, holding off any extreme cold air outbreaks like those seen during the last two winters.
Hazardous weather. No hazardous weather was reported in the state during December 2011.
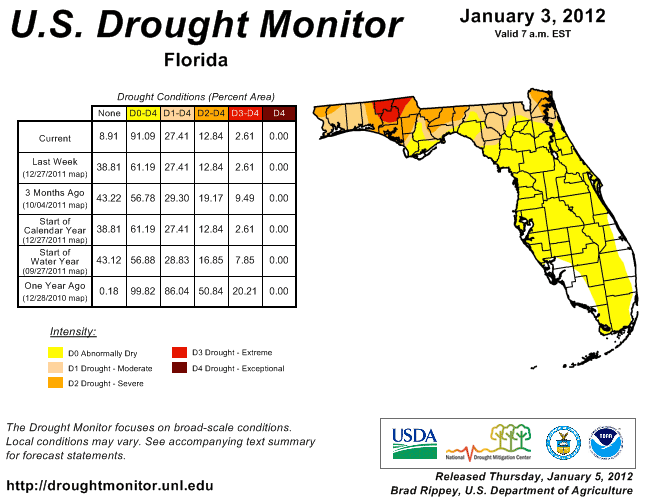
Agricultural and other impacts. Winter planting progressed due to dry conditions, with good growth evident in may winter crops due to mild temperatures. Ryegrass was not planted, due to La Niña, and most of the livestock in the state is being fed hay and supplements. Since the November 29 release of the National Drought Monitor, there have been some large changes to the status of the drought in Florida. The area of extreme drought that lingered in parts of the Panhandle eased after some areas received above normal rainfall during December. However, portions of the Peninsula had drier than normal conditions during December. At the end of November, only about 37% of the state was under any type of drought designation. That number has now increased to just over 91%. Continued La Niña conditions through the winter will mean decreased precipitation, and water restrictions remain in place in South Florida (the water level of Lake Okeechobee is now 13.55 ft). Restrictions in other areas could go into effect.
Figure 2: Drought conditions in Florida as of January 3, 2012 (courtesy of U.S. Drought Monitor).
Appendix: Daily maximum and minimum temperature records (° F) tied or broken during December (compiled from NOAA, NWS).